Seamless support from diagnosis to post treatment care
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition caused by the excessive buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the skull. This increases the pressure inside the brain. CSF’s primary function is to cushion and protect the brain, but when an excess of it is accumulated, it can damage brain tissue and cause developmental, physical, and cognitive disorders.
Hydrocephalus most commonly occurs in infants and adults over 60, but it can also affect young adults. In congenital cases, an abnormally large head is the first noticeable sign.
Causes
The level of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain can increase due to the following reasons:
- A blockage that prevents normal CSF flow
- Overproduction of CSF by the brain
- Reduced absorption of CSF by blood vessels
Hydrocephalus can be congenital (present at birth) or develop later in life due to conditions such as:
- Birth defects
- Genetic abnormalities
- Infections during pregnancy, such as rubella
- Meningitis, particularly in infants
- Bleeding in the brain before, during, or after delivery
- Central nervous system tumors
- Head injuries or trauma
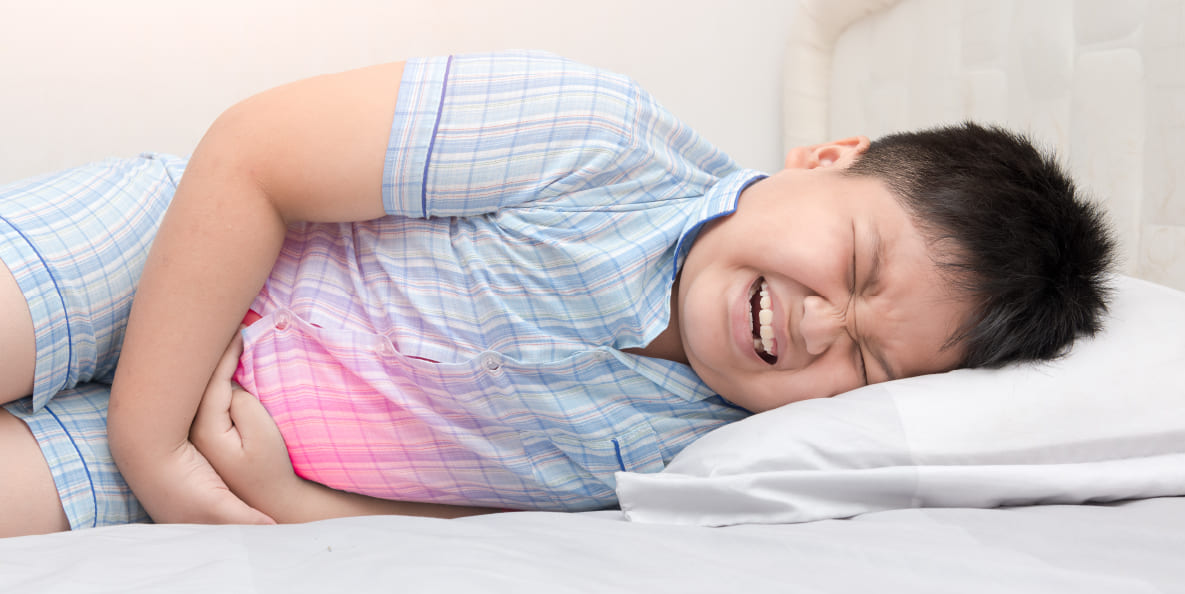
Signs and Symptoms
Hydrocephalus can be life-threatening if not treated in a timely manner. So, early detection is crucial.
In infants, the signs may include:
- A bulging soft spot (fontanelle) on the skull
- Unusual enlargement of the head
- Seizures
- Vomiting
- Not feeding properly
- Weak muscles
In toddlers and children, the symptoms can include:
- High-pitched crying
- Personality changes
- Changes in facial structure
- Crossed eyes
- Persistent headaches
- Delayed growth and development
- Difficulty in eating
- Loss of coordination or balance
- Loss of bladder control
- Vomiting and nausea
- Seizures
In young and middle-aged adults, symptoms include:
- Chronic headaches
- Balance and coordination problems
- Difficulty walking
- Problem in bladder control
- Problems with Vision
- Difficulties in memory and concentration
Diagnosis and Treatment
To diagnose hydrocephalus, a neurosurgeon will order following tests:
- Ultrasound
- CT scans
- MRI scans
These tests help to reveal enlarged brain ventricles caused by excess CSF.
Surgical Treatment
If left untreated, hydrocephalus can be fatal. While treatment cannot reverse existing brain damage, it can prevent further complications and restore normal CSF flow.
Surgical treatments include:
- Shunt Insertion: The shunt is a drainage system made of a long tube with a valve through which excess fluid is drained out either into the patient's chest or abdominal cavity. A shunt implant is permanent and needs to be checked regularly.
- Ventriculostomy (Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy - ETV): A minimally invasive procedure where a small hole is made in a brain ventricle to allow CSF to drain naturally.
Why Choose Us?
At Rainbow Children’s Hospital, we are dedicated to providing world-class pediatric neurosurgical care, ensuring the best possible outcomes for children with hydrocephalus.
Here’s what makes us the most preferred choice:
- Expert Pediatric Neurosurgery Team: Our highly skilled pediatric neurosurgeons specialize in treating complex brain and spinal conditions, using both traditional and minimally invasive techniques.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: We are equipped with cutting-edge facilities, including high-resolution imaging, intraoperative monitoring, and advanced neurosurgical tools like neuronavigation and endoscopic systems.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Our team works closely with pediatric neurologists, neonatologists, intensive care specialists, and rehabilitation experts to provide holistic care.
- 24/7 Emergency Care: We are always prepared to handle neurosurgical emergencies, ensuring immediate and expert intervention when needed.
- Child-Centric Care: With a compassionate approach, we create a child-friendly environment that helps young patients feel at ease throughout their treatment journey.

Find a Doctor
Expertise you can trust, Meet our esteemed doctors who bring exceptional knowledge, compassion, and innovation to provide top-notch care for your health and well-being.
Our Hospitals and ClinicsOur Hospitals and Clinics
Rainbow Children's Hospital stands as a testament to the hospital's continual pursuit of excellence and innovation, providing specialized care for women and children.
Request a Call back
Tap to Fill FormRequest a Call back
Blogs
Discover our most recent health articles provided by our reliable experts.
What Are People Saying About Us
Embark on a journey of inspiration and hope with our patient success stories, complemented by informative videos from our dedicated doctors.
Quick Links
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeons in Hyderabad
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeon In Bangalore
- Pediatric Neurosurgeon in Delhi
- Pediatric Neurosurgeons in Chennai
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeon in Vijayawada
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeon in Vizag
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeon in Hyder Nagar
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeon in Marathahalli
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeons in Guindy
- Best Pediatric Neurosurgeons in Currency Nagar
- Best Pediatric Neurosureon in Banjarahills
- Top Pediatric Neurosurgeons in India
- Spina Bifida in Children, Hyderabad
- Spinal Cord Injury in Children, Hyderabad
- Arachnoid Cysts in Children, Hyderabad
- Chiari Malformation in Children, Hyderabad
- Glioblastoma Multiforme in Children, Hyderabad
- Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Children, Hyderabad
- Deep Brain Stimulation in Children, Hyderabad
- Oligodendroglioma in Children, Hyderabad
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Children, Hyderabad
- Skeletal Dysplasia in Children, Hyderabad
- Laser Ablation in Children, Hyderabad
- Radiosurgery in Children, Hyderabad
- Tethered Spinal Cord in Children, Hyderabad
- Cavernous Malformations in Children, Hyderabad
- Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor in Children, Hyderabad
- Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy in Children, Hyderabad
- Pial Synangiosis in Children, Hyderabad
- Metopic Synostosis Trigonocephaly in Children, Hyderabad
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET) in Children, Hyderabad
- Vein of Galen Malformation (VOGM) in Children, Hyderabad
- Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) in Children, Hyderabad
- Spina Bifida in Children, Bengaluru
- Spinal Cord Injury in Children, Bengaluru
- Arachnoid Cysts in Children, Bengaluru
- Chiari Malformation in Children, Bengaluru
- Glioblastoma Multiforme in Children, Bengaluru
- Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Children, Bengaluru
- Deep Brain Stimulation in Children, Bengaluru
- Oligodendroglioma in Children, Bengaluru
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Children, Bengaluru
- Skeletal Dysplasia in Children, Bengaluru
- Laser Ablation in Children, Bengaluru
- Radiosurgery in Children, Bengaluru
- Tethered Spinal Cord in Children, Bengaluru
- Cavernous Malformations in Children, Bengaluru
- Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor in Children, Bengaluru
- Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy in Children, Bengaluru
- Pial Synangiosis in Children, Bengaluru
- Metopic Synostosis Trigonocephaly in Children, Bengaluru
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET) in Children, Bengaluru
- Vein of Galen Malformation (VOGM) in Children, Bengaluru
- Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) in Children, Bengaluru
- Spina Bifida in Children, Delhi
- Spinal Cord Injury in Children, Delhi
- Arachnoid Cysts in Children, Delhi
- Chiari Malformation in Children, Delhi
- Glioblastoma Multiforme in Children, Delhi
- Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Children, Delhi
- Deep Brain Stimulation in Children, Delhi
- Oligodendroglioma in Children, Delhi
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Children, Delhi
- Skeletal Dysplasia in Children, Delhi
- Laser Ablation in Children, Delhi
- Radiosurgery in Children, Delhi
- Tethered Spinal Cord in Children, Delhi
- Cavernous Malformations in Children, Delhi
- Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor in Children, Delhi
- Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy in Children, Delhi
- Pial Synangiosis in Children, Delhi
- Metopic Synostosis Trigonocephaly in Children, Delhi
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET) in Children, Delhi
- Vein of Galen Malformation (VOGM) in Children, Delhi
- Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) in Children, Delhi
- Spina Bifida in Children, Chennai
- Spinal Cord Injury in Children, Chennai
- Arachnoid Cysts in Children, Chennai
- Chiari Malformation in Children, Chennai
- Glioblastoma Multiforme in Children, Chennai
- Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Children, Chennai
- Deep Brain Stimulation in Children, Chennai
- Oligodendroglioma in Children, Chennai
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Children, Chennai
- Skeletal Dysplasia in Children, Chennai
- Laser Ablation in Children, Chennai
- Radiosurgery in Children, Chennai
- Tethered Spinal Cord in Children, Chennai
- Cavernous Malformations in Children, Chennai
- Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor in Children, Chennai
- Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy in Children, Chennai
- Pial Synangiosis in Children, Chennai
- Metopic Synostosis Trigonocephaly in Children, Chennai
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET) in Children, Chennai
- Vein of Galen Malformation (VOGM) in Children, Chennai
- Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) in Children, Chennai
- Spina Bifida in Children, Vijayawada
- Spinal Cord Injury in Children, Vijayawada
- Arachnoid Cysts in Children, Vijayawada
- Chiari Malformation in Children, Vijayawada
- Glioblastoma Multiforme in Children, Vijayawada
- Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Children, Vijayawada
- Deep Brain Stimulation in Children, Vijayawada
- Oligodendroglioma in Children, Vijayawada
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Children, Vijayawada
- Skeletal Dysplasia in Children, Vijayawada
- Laser Ablation in Children, Vijayawada
- Radiosurgery in Children, Vijayawada
- Tethered Spinal Cord in Children, Vijayawada
- Cavernous Malformations in Children, Vijayawada
- Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor in Children, Vijayawada
- Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy in Children, Vijayawada
- Pial Synangiosis in Children, Vijayawada
- Metopic Synostosis Trigonocephaly in Children, Vijayawada
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET) in Children, Vijayawada
- Vein of Galen Malformation (VOGM) in Children, Vijayawada
- Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) in Children, Vijayawada
- spina-bifida-in-children-vizag
- spinal-cord-injury-in-children-vizag
- arachnoid-cysts-in-children-vizag
- chiari-malformation-in-children-vizag
- glioblastoma-multiforme-in-children-vizag
- intraventricular-hemorrhage-in-children-vizag
- deep-brain-stimulation-in-children-vizag
- oligodendroglioma-in-children-vizag
- pilocytic-astrocytoma-in-children-vizag
- skeletal-dysplasia-in-children-vizag
- laser-ablation-in-children-vizag